
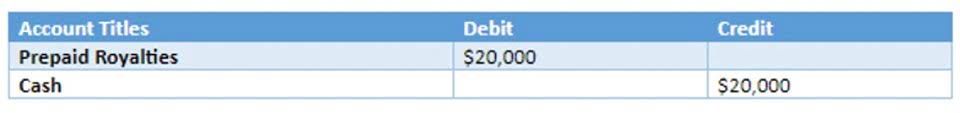
Any set standard can be easily modified to meet the changing business environment and needs. For small or sole proprietary businesses, the owner of a business is usually part of the management. Nonetheless, information from managerial accounting is used by the internal administrators of a company that make the decisions. The area of managerial accounting that attracts the most focus is cost accounting.
- Managerial accounting information is aimed at helping managers make well-informed business decisions on the direction of the company.
- The end result of budgeting is a budget, a document that shows the business’ commitment to execute plans, acquire resources, and use resources.
- The primary focus of managerial accounting is ensuring that a company has all the information required to make sound decisions that limit risk and maximize profits.
- It also empowers them to optimize resource allocation, assess performance, and identify improvement areas.
- Account receivables are the invoices or credits which a company expects to be remunerated by its debtors.
- These accountants serve as vital liaisons between upper-level management of a business enterprise and employees.
- Accountants use a variety of calculations to assess the value and return on investment the proposed capital investment offers.
Management accountants
Decision-making involves analyzing data, evaluating alternatives, and making informed choices to achieve organizational goals. One planning tool is the budgeting process, which requires management to assess the resources—for example, time, money, and number and type of employees needed—to meet current-year objectives. Budgeting often includes both financial data, such as worker pay rates, and nonfinancial data, such as the number of customers an employee can serve in a given time period. The first principle is that the data provided by a managerial accountant should be relevant. By doing this managers can obtain the necessary data to inform their decisions.Third, accountants must be able to analyze the efficiency of their managerial accounting operations and identify the scope for improvements. By assessing opportunities and risks, they should be able to run simulations on the data to predict future outcomes and determine which outcome is best pursued.

Jobs in Managerial Accounting
These internal users may include management at all levels in all departments, owners, and other employees. For example, in the budget development process, a company such as Tesla may want to project the costs of producing a new line of automobiles. Although outside parties might be interested in this information, companies like Tesla, Microsoft, and Boeing spend significant amounts of time and money to keep their proprietary information secret. Therefore, these internal budget reports are only available to the appropriate users. The main difference between managerial accounting and financial accounting is the parties for which they provide financial information.
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis

However, knowledge of GAAP principles can be beneficial in ensuring accurate and consistent financial information for managerial analysis. While managerial accounting incorporates non-financial performance indicators, there can be a tendency to focus excessively on financial metrics. This may lead to overlooking critical non-financial factors that contribute to long-term organizational success, such as customer satisfaction, employee engagement, innovation, and sustainability. It involves monitoring aging receivables, setting credit policies, and implementing effective collection practices to improve cash flow and minimize bad debts. By efficiently managing AR, businesses can enhance cash flow, maintain healthy customer relationships, and reduce non-payment risk.
- For example, if a department manager is considering purchasing a company vehicle, he may have the option to either buy the vehicle outright or get a loan.
- In each of these examples, the managerial accounting function would help to determine the variables that would help appropriately measure the desired goal as well as plan how to quantify these measures.
- For example, small businesses can conduct financial statement analysis to assess the business’ liquidity, solvency, and performance before applying for a small business loan.
- Regardless of where you are in your career, you can find an option that is within your reach.
- At any level, managers work closely with the managerial accounting team to help in each of these stages.
- It involves analyzing value chains, conducting activity-based costing, and identifying cost drivers that impact the organization’s competitive advantage.
GAAP may be a deterrent to getting useful information for internal decision-making purposes. However, for internal decision-making purposes, it might make more sense to include nonproduction costs that are directly linked to the product, such as sales commissions or administrative costs. Three friends who are recent graduates from business school, Alex, Hana, and Gillian, have each just begun their first postgraduation jobs.
- By comparing budgets with actual results, managers and small business owners can assess if the employees are performing accordingly.
- Inventory turnover is the measure of the inventory a business sold or used within a given time period.
- In addition, managerial accounting uses nonfinancial data, whereas financial accounting relies solely on financial data.
- Cost accounting is used to measure and identify those costs, in addition to assigning overhead to each type of product created by the company.
- While there are several reports that are created on a regular basis (e.g., budgets and variance reports), many management reports are produced on an as-needed basis.
Since managerial accounting is used for internal purposes only, it is not required to conform with accounting standards, such as GAAP. The balanced scorecard is a concept developed to measure performance by combining financial and nonfinancial metrics. The approach can be useful for small businesses to provide a holistic evaluation of performance for employees and managers. Tools like segment margins and return on investment (ROI) can help you evaluate the performance of specific departments. A segmented income statement presents income and expenses pertaining to the particular segment or department, and this income statement can measure the department manager’s efficiency and effectiveness.
Trend analysis examines historical data to identify patterns and changes over time. Forecasting utilizes historical trends and external factors to predict future performance. These techniques allow businesses to make informed decisions, predict market changes, and create future growth plans. Managerial accounting involves assigning costs to products, services, or activities using different costing methods, such as job costing, process costing, or activity-based costing. This helps determine accurate product costs, assess profitability, and make pricing decisions.

This information helps organizations better understand how well they adhere to set budgets and make changes if needed. Another aspect of this methodology is examining an organization’s needs, choosing the correct purchase type, and finding the best way to finance that purchase. While managerial accounting focuses on providing data for internal use, financial accounting focuses on the decisions managerial accounting related to an organization’s financial relationship with external companies. Evaluating, also called assessing or analyzing, involves comparing actual results against expected results, and it can occur at the product, department, division, and company levels. The key difference between managerial accounting and financial accounting relates to the intended users of the information.